The Toyota Production System is renowned worldwide as a benchmark for lean manufacturing and operational excellence. Developed by Toyota, one of the leading automotive manufacturers, this system has revolutionized the way organizations approach production and efficiency.
At the heart of the Toyota Production System is the philosophy of continuous improvement and waste reduction. By eliminating waste and streamlining processes, Toyota has been able to achieve remarkable results in terms of cost reduction, quality improvement, and customer satisfaction.
Lean manufacturing, as implemented by Toyota, focuses on maximizing value while minimizing waste. This approach involves the relentless pursuit of efficiency, from the design and planning stages to the production line and beyond. Every step in the production process is carefully analyzed and optimized to ensure that resources are utilized effectively and efficiently.
Key principles of the Toyota Production System include:
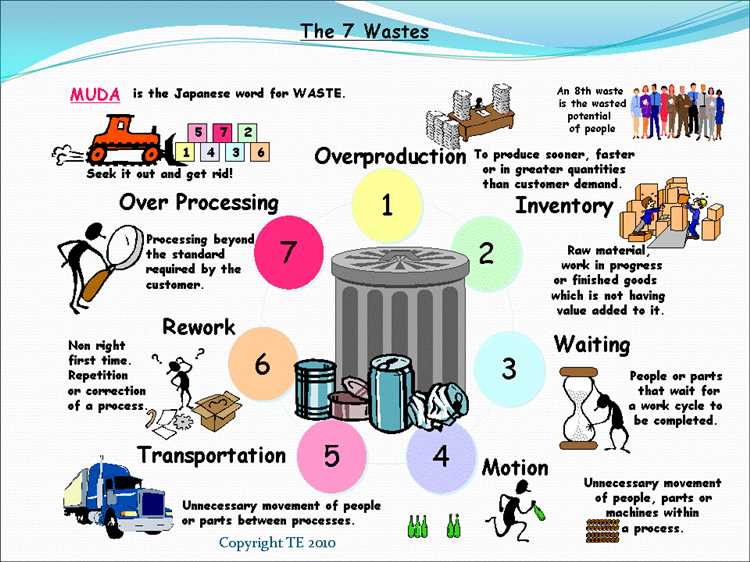
1. Just-in-time production: By producing only what is needed, when it is needed, Toyota minimizes inventory and avoids overproduction.
2. Jidoka: This principle emphasizes automation with a human touch, empowering employees to stop the production line whenever a problem is detected.
3. Kaizen: Continuous improvement is ingrained in Toyota’s culture, with employees encouraged to identify and implement small, incremental changes to improve efficiency and quality.
4. Poka-yoke: Mistake-proofing processes and systems to prevent errors and defects from occurring, reducing waste and improving overall quality.
By embracing the Toyota Production System, businesses can unlock their full potential and achieve sustainable growth. The system has proven to be adaptable across industries, from manufacturing to healthcare and beyond, making it a powerful tool for any organization looking to drive operational excellence.
Experience the power of lean manufacturing with the Toyota Production System and join the ranks of successful organizations that have transformed their operations and achieved unparalleled results.
The Toyota Production System

The Toyota Production System is a world-renowned manufacturing methodology that has revolutionized the automotive industry. With its foundation in lean manufacturing principles, it focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing efficiency to deliver high-quality products to customers.
One of the key principles of the Toyota Production System is just-in-time production, which aims to minimize inventory levels and reduce the cost of holding inventory. By producing only what is needed, when it is needed, Toyota is able to avoid overproduction and reduce lead times, resulting in significant cost savings.
Another important aspect of the Toyota Production System is continuous improvement, also known as kaizen. This involves constantly seeking ways to improve processes, eliminate waste, and empower employees to contribute to the overall success of the organization. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, Toyota is able to stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.
The Toyota Production System also emphasizes the importance of standardization and visual management. Standardized work processes help to ensure consistency and reliability in production, while visual management tools such as Kanban boards and Andon systems allow for real-time monitoring of production status and immediate problem-solving.
In summary, the Toyota Production System is a comprehensive approach to manufacturing that has revolutionized the industry. By embracing lean principles, continuous improvement, and visual management, Toyota has been able to achieve unparalleled levels of efficiency and quality. Whether you are in the automotive industry or any other manufacturing sector, implementing the Toyota Production System can help you achieve similar success.
The origins of TPS
The Toyota Production System (TPS) is a renowned manufacturing philosophy developed by Toyota that has revolutionized the automotive industry. It originated in Japan in the 1940s and 1950s, when Toyota faced several challenges due to the post-World War II economic crisis and limited resources.
During this time, Toyota’s founder, Kiichiro Toyoda, and his team realized the need for a more efficient and flexible production system that could adapt to changing customer demands and optimize the use of available resources. They drew inspiration from various sources, including the principles of American supermarkets and the production methods of Ford Motor Company.
One of the key principles of TPS is the concept of “Just-in-Time” (JIT) production, which emphasizes the timely delivery of materials and components to the production line, reducing inventory and waste. This approach was a radical departure from the traditional mass production model, where large inventories were maintained to ensure uninterrupted production.
Another fundamental concept of TPS is “Kaizen,” which means continuous improvement. Toyota recognized the importance of empowering its employees to identify and solve problems on the production line, leading to incremental improvements that collectively have a significant impact on efficiency and quality.
Over the years, TPS has been refined and adopted by numerous industries worldwide, beyond automotive manufacturing. Its principles of waste reduction, quality improvement, and employee empowerment have become the cornerstone of lean manufacturing and have contributed to the success of many organizations.
The philosophy behind TPS
The Toyota Production System (TPS) is built on a philosophy of continuous improvement and waste reduction. It aims to eliminate any activities or processes that do not add value to the final product or service. This philosophy is based on the belief that by identifying and eliminating waste, companies can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately provide better products and services to their customers.
One of the core principles of TPS is the concept of “Just-in-Time” production. This means producing goods or services exactly when they are needed, in the quantities required, and at the highest level of quality. By minimizing inventory and reducing lead times, companies can eliminate the cost of carrying excess inventory and respond quickly to changes in customer demand.
Another key principle of TPS is “Respect for People.” This means creating a work environment that values the contributions of every employee and encourages their active participation in improving processes and solving problems. By empowering employees and fostering a culture of continuous learning, companies can tap into the creativity and expertise of their workforce, leading to better ideas and more innovative solutions.
TPS also emphasizes the importance of standardization and visual management. By clearly defining standard work processes and making them visible to all employees, companies can ensure consistency and reduce variation in their operations. This not only leads to higher quality products and services, but also makes it easier to identify and resolve any issues or bottlenecks that arise.
In summary, the philosophy behind TPS is centered around continuous improvement, waste reduction, just-in-time production, respect for people, and standardization. By embracing these principles, companies can create a culture of excellence and achieve sustainable success in today’s competitive business environment.
The key principles of TPS
1. Just-in-Time (JIT) Production: TPS focuses on producing only what is necessary, when it is necessary, and in the quantity that is necessary. By eliminating waste and reducing inventory, JIT production allows for smoother operations and reduced costs.
2. Jidoka: This principle emphasizes the importance of building quality into the production process. Jidoka allows for immediate detection of any defects or abnormalities, enabling quick response and preventing the production of defective products.
3. Standardized Work: TPS places great importance on defining and documenting the best practices and standardizing work processes. This helps to eliminate variations, improve efficiency, and ensure consistent quality.
4. Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): TPS encourages a culture of continuous improvement, where everyone is involved in identifying and implementing small improvements on a daily basis. This mindset of continuous learning and problem-solving helps to drive innovation and enhance overall performance.
5. Respect for People: TPS values the contributions of every individual and emphasizes the importance of teamwork and mutual respect. By empowering employees, providing them with training and support, and fostering a positive work environment, TPS creates a culture of engagement and motivation.
6. Visual Management: TPS utilizes visual tools and displays to provide real-time information and make it easy for employees to understand the status of operations and identify any issues. This helps to improve communication, increase transparency, and facilitate effective decision-making.
7. Supplier Involvement: TPS recognizes the importance of strong relationships with suppliers and actively involves them in the production process. By working closely with suppliers to share information, collaborate on improvements, and ensure timely delivery of materials, TPS optimizes the entire supply chain.
8. Poka-Yoke (Error Proofing): TPS employs devices and mechanisms to prevent errors and mistakes from occurring. Poka-yoke systems help to minimize defects, reduce rework, and improve overall quality.
Implementation of TPS
Implementing the Toyota Production System (TPS) is a strategic decision that can greatly benefit any manufacturing organization. By adopting the TPS principles and practices, companies can improve their operational efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance overall productivity.
One key aspect of TPS implementation is the establishment of standardized work processes. This involves defining clear instructions and procedures for each step of the production process, ensuring that all employees understand their roles and responsibilities.
Another important element of TPS implementation is the concept of just-in-time (JIT) production. This means producing and delivering products to customers exactly when they are needed, without excess inventory or delays. By implementing JIT, companies can minimize inventory costs, reduce lead times, and improve customer satisfaction.
TPS also emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement. This involves constantly seeking ways to eliminate waste, streamline processes, and enhance quality. By implementing a culture of continuous improvement, companies can foster innovation, empower employees, and drive sustainable growth.
Furthermore, TPS implementation requires strong leadership and employee involvement. Managers should provide guidance and support, while employees should actively participate in problem-solving and decision-making processes. This collaborative approach helps create a culture of teamwork and accountability, leading to better outcomes.
In conclusion, implementing the Toyota Production System brings numerous benefits to manufacturing organizations. By adopting standardized work processes, implementing just-in-time production, emphasizing continuous improvement, and fostering a culture of collaboration, companies can achieve operational excellence and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Training and education
At Toyota, we understand the importance of training and education in developing a highly skilled and efficient workforce. We offer a comprehensive range of training programs designed to enhance the knowledge and skills of our employees.
Our training programs cover various aspects of lean manufacturing, including the Toyota Production System, quality control, problem-solving techniques, and continuous improvement. Through hands-on training and classroom sessions, our employees gain a deep understanding of the principles and practices that drive our success.
We believe in empowering our employees with the knowledge and skills they need to excel in their roles. That’s why we invest in continuous education and provide opportunities for professional development. We offer advanced training programs for our team leaders and managers, equipping them with the tools and strategies to lead their teams to success.
In addition to our internal training programs, we also collaborate with external organizations and universities to offer specialized courses and workshops. This allows our employees to stay updated with the latest industry trends and best practices.
Through our commitment to training and education, we ensure that our employees are equipped with the knowledge and skills to deliver high-quality products and services to our customers. Join us and become part of a learning organization that values continuous improvement and personal growth.
Continuous Improvement
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment, staying ahead of the game is crucial. In order to remain competitive, companies must constantly adapt and improve their processes to meet changing customer demands and market conditions. This is where continuous improvement comes in.
Continuous improvement is a philosophy and methodology that focuses on making small, incremental changes to processes in order to achieve greater efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. It is a never-ending journey that involves every employee from the top management to the shop floor workers.
At its core, continuous improvement is about challenging the status quo and constantly looking for ways to do things better. It encourages employees to identify and eliminate waste, streamline processes, and find innovative solutions to problems. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, companies can drive innovation, increase productivity, and ultimately, achieve sustainable growth.
Implementing continuous improvement requires a structured approach. It involves setting clear goals and objectives, measuring performance, analyzing data, and implementing changes based on the findings. It also requires strong leadership and employee engagement, as everyone in the organization has a role to play in driving continuous improvement.
By embracing continuous improvement, companies can stay ahead of the competition, deliver higher quality products and services, and create more value for their customers. It is a powerful tool that allows companies to adapt to changing market conditions, improve operational efficiency, and achieve long-term success.
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Reduced waste and cost
- Improved quality and customer satisfaction
- Enhanced employee engagement and morale
Continuous improvement is not just a buzzword, but a strategic approach that can transform businesses and drive them towards excellence. By making continuous improvement a part of their DNA, companies can achieve sustainable growth and create a culture of innovation and success.
Standardization and visual management

Standardization is a key element of the Toyota Production System, ensuring consistency and quality across all processes. By standardizing work procedures, Toyota minimizes the risk of errors and variations, leading to improved efficiency and productivity. Standardization also allows for easier training of new employees, as they can quickly learn and follow established procedures.
Visual management is another important aspect of the Toyota Production System. It involves the use of visual cues, such as color-coding, signage, and labels, to provide information and instructions to workers. These visual cues make it easier for employees to understand and follow procedures, reducing the likelihood of mistakes and improving overall operational efficiency.
One example of visual management in action is the use of kanban boards. Kanban is a Japanese term for “visual signal” or “card,” and kanban boards are used to visually represent the flow of work in a production process. These boards typically have columns representing different stages of production, with cards or magnets representing individual tasks or items. The movement of these cards or magnets across the board provides a visual representation of the progress of work, allowing for easy identification of bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
In addition to kanban boards, Toyota also utilizes visual management techniques such as Andon boards and shadow boards. Andon boards display real-time information about the status of production processes, helping to identify and resolve issues quickly. Shadow boards, on the other hand, provide a designated place for tools and equipment, ensuring that everything is properly stored and easily accessible.
Overall, standardization and visual management play crucial roles in the success of the Toyota Production System. By implementing these practices, Toyota is able to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and ensure consistent quality in their manufacturing processes.